what is the name of the 32-bit or 128-bit number that is used to identify a device on a network
This tutorial explains IP accost, network address, host address, and subnet mask in item. Acquire what IP addresses are and how they work in computer networks.
If objects connected in a grouping desire to share or exchange something, they demand a specific identity to refer to each other. This unique identity is known as the address. In unproblematic terms, addresses are a way of organizing and locating objects in a single group or multiple groups. Addresses are mainly used for two reasons: to provide a unique identity to each object in the grouping and to find an object in the group.
A reckoner network is a group of computers and various networking devices that connect to share information and resources. To uniquely identify each computer or networking device in the network, calculator networks likewise utilize addresses. Addresses in calculator networks are known equally IP addresses. An IP address consists of two components: the network address and the host address. The network accost is used to find the subnet in which the reckoner or the device is located and the host accost is used to find the reckoner or the device in the subnet. If a large computer network is divided into smaller groups, each group is known equally a subnet.
IP addresses tin be written in three notations: binary, dotted-decimal, and hexadecimal. From these notations, computers sympathise only binary notation. Binary notation is circuitous to write and understand. To make IP addresses human friendly, IP addresses are besides written in dotted-decimal and hexadecimal notations. If IP addresses are written in dotted-decimal notation or hexadecimal annotation, computers automatically catechumen them into binary notation before processing them.
There are two versions of IP addresses: IPv4 and IPv6. The length of IP addresses is unlike in both versions. Both versions besides apply different formats to differentiate between network addresses and host addresses. Allow's understand IP addresses in both versions.
IP addresses in IPv4
IPv4 addresses are 32 $.25 in length. These bits are divided into four equal sections. Sections are separated by periods and written in a sequence. In measurement, eight bits are equal to one byte or an octet. In simple words, an IP accost consists of iv bytes or octets separated by periods.
The post-obit image shows how $.25 are arranged in IPv4 addresses.
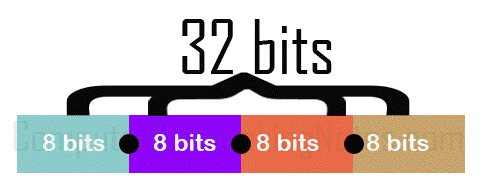
In binary notation, all four octets are written in binary format. For example, some IP addresses in binary format are listed below.
00001010.00001010.00001010.00001010 10101100.10101000.00000001.00000001 11000000.10101000.00000001.00000001
IPv4 addresses are written and used in dotted-decimal notation. In decimal notation, all iv octets are written in decimal format. A decimal equivalent value of the octet is used in each section. For example, you lot can write the above IP addresses in decimal notation as shown below.
10.10.10.10 172.168.one.one 192.168.1.1
Subnet Mask
To dissever network addresses from host addresses, IPv4 uses an additional component with IP addresses. This component is known as a subnet mask. In other words, in an IP address, how many bits are used in the network address and how many bits are left for the host address is adamant by the subnet mask. The subnet mask is too 32 bits in length and uses the same annotation that is used by the IP address.
The subnet mask assigns an private bit for each flake of the IP accost. If an IP bit belongs to the network portion, the subnet mask volition plough on the assigned flake. If an IP bit belongs to the host portion, the subnet mask will turn off the assigned chip.
In binary annotation, 1 (one) represents an ON chip while 0 (null) represents an OFF bit. In dotted-decimal notation, a value range 1 to 255 represents an ON scrap while a value 0 (nada) represents an OFF chip.
Following are the examples of subnet mask in binary notation: -
11111111.00000000.00000000.00000000 11111111.11111111.00000000.00000000 11111111.11111111.11111111.00000000
Following are the examples of subnet mask in decimal notation: -
255.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 255.255.255.0
An IP accost is e'er used with the subnet mask. Without the subnet mask, an IP address is considered an cryptic address.
Following are the examples of IP addresses with subnet mask in binary annotation: -
00001010.00001010.00001010.00001010 11111111.00000000.00000000.00000000 10101100.10101000.00000001.00000001 11111111.11111111.00000000.00000000 11000000.10101000.00000001.00000001 11111111.11111111.11111111.00000000
Following are the examples of IP addresses with subnet mask in decimal note: -
ten.ten.ten.x 255.0.0.0 172.168.i.i 255.255.0.0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
The following image shows how the subnet mask dissever the network accost from the host accost in an IP address.

IP addresses in IPv6
IPv6 addresses are 128 $.25 in length. These bits are divided into eight equal sections. Sections are separated past colons (:) and written in a sequence. IPv6 addresses are written in hexadecimal notation.
The following prototype shows how bits are arranged in IPv6 addresses.
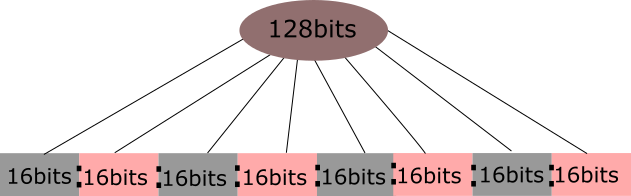
Following are the examples of IP addresses in IPv6: -
2001:1238:85b3:0000:0000:a82e:aa70:7124 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a11:0121:6213 2001:0db8:0000:85a3:8a3d:2122:0000:1542 2001:0000:0db8:85a3:0000:8a2c:3233:3312
Instead of using an additional component to dissever network addresses and host addresses, IPv6 defines the number of $.25 for both types of addresses. It defines the first 64 bits equally the network address and the concluding 64 bits as the host accost.
The following image shows how IPv6 separates the network address and host accost in an IP address.

How do host addresses work?
In calculator networks, IP addresses are assigned on interfaces. An interface connects a computer or a networking device to the network. In a computer network, all interfaces must be configured with unique IP addresses. If two or more than interfaces are configured with the aforementioned IP address, the network will non work.
Permit'south sympathize information technology through an example.
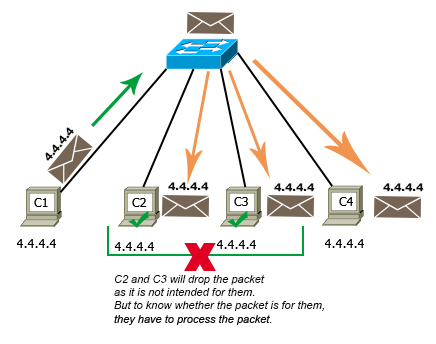
In a figurer network, four computers named C1, C2, C3, and C4 are continued. All computers are configured with the same IP address. The configured IP address is four.four.4.4/8. C1 sends a data packet to C4. Since the IP address of C4 is 4.4.4.4/8, C1 sets the destination address in the packet to 4.iv.4.4/viii.
The packet reaches C2, C3, and C4. They check the destination address of the packet to know whether the packet is intended for them. Since the destination address of the packet matches with the IP address configured on their interfaces, they all assume that the package is intended for them, and they all procedure it.
After processing, C2 and C3 realize that the packet is non intended for them and they discard the packet. C4 accepts the bundle. If C4 sends a reply packet, the reply packet will besides follow the same path and will be processed by C2 and C3 unnecessarily.
The following epitome shows this case.
In a busy network where interfaces process millions of packets per second, an overlap of IP addresses tin can bring the entire network downward. To avoid such a situation, computer networks apply a unique IP accost on each interface.
Allow's take our example network over again and make all IP addresses unique. To make all IP addresses unique, change their host addresses. For example, you tin can set up the new IP addresses of C1, C2, C3, and C4 to 4.4.4.i/8, 4.four.four.two/8, 4.iv.4.3/8, and 4.four.4.4/viii, respectively.
After this alter, when C1 sends packets to C4 and the parcel reaches C2, C3, and C4, but C4 processes the packet. C2 and C3 immediately discard the packet because the destination address of the packet and the IP address of their interfaces are different.
The following image shows how a host address works in the network.
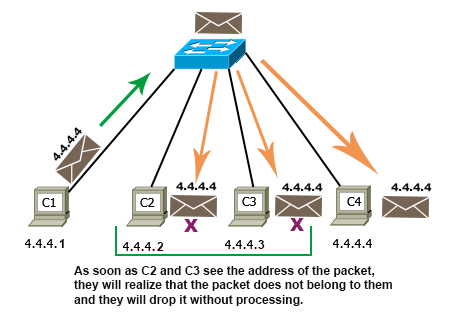
If all interfaces are configured with unique IP addresses, they can access each other easily.
How practice network addresses piece of work?
Just as a host address provides a unique identity to the interface in a subnet, a network address provides a unique identity to the subnet in the network. A network address is the common address of all interfaces that vest to a specific subnet.
Allow's take an instance to sympathise how network addresses piece of work.
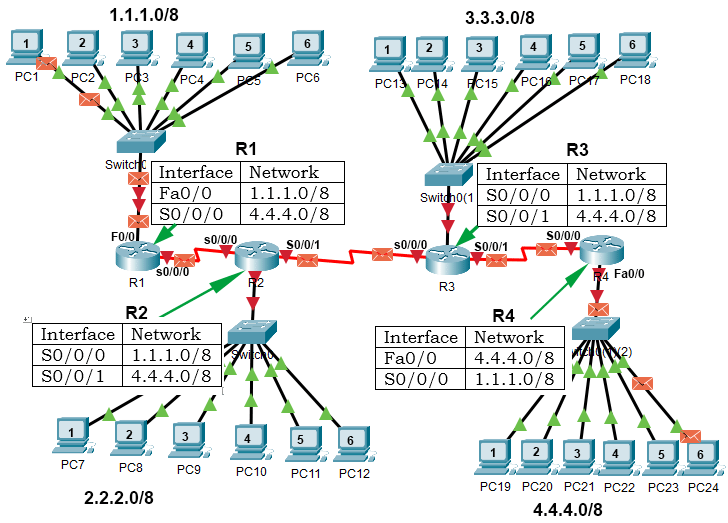
In a network, 4 subnets are connected. Network addresses of these subnets are ane.1.1, 2.2.2, 3.3.iii, and four.4.four. Each subnet contains vi PCs. Host addresses of PC1, PC2, PC3, PC4, PC5, and PC6 are .one, .2, .3, .4, .5, and .6, respectively.
In IP addresses, network addresses are always written earlier host addresses. If nosotros write the network address before the host address of a PC, we will become the IP address of that PC. The following image shows this process in our example network.

Hosts or PCs of different subnets cannot communicate or exchange data directly. To connect different subnets, routers are used. Routers are networking devices that connect different subnets or networks. Routers shop the network addresses of all available subnets in their routing tables.
If a computer wants to send a data packet to a computer that belongs to another subnet, information technology sends the data package to the gateway router. A gateway router is the router that connects the subnet to other subnets of the network. The gateway router forwards the data parcel to the router that is connected to the destination subnet or know how to achieve the destination subnet. To frontwards information packets, routers apply merely network addresses.
Let's understand information technology through our example. Our case network is divided into four subnets. To connect these subnets, iv routers: R1, R2, R3, and R4 are used. R1, R2, R3, and R4 are connected to the first subnet (1.1.one.0/8), 2d subnet (ii.2.2.0/8), third subnet (3.3.3.0/eight), and the fourth subnet (4.4.4.0/8), respectively.
Now suppose, PC1 of the starting time subnet sends a data packet to PC6 of the fourth subnet. PC1 sets destination IP address in the parcel to 4.iv.iv.6/8. In this IP address, four.4.iv is the network address and .6 is the host address. The packet reaches R1. R1 checks its routing table and forrad the packet to R2. R2 follows the same procedure and forwards the packet to R3. R3 forrard the parcel to R4 and R4 forwards the packet to the local network of the fourth subnet. The local network of the 4th subnet uses the host address of the packet to observe the PC6.
The post-obit image shows this process.
If you like this tutorial, please share it with friends via your favorite social networking sites and subscribe to our YouTube aqueduct.
Source: https://www.computernetworkingnotes.com/networking-tutorials/ip-address-network-address-and-host-address-explained.html
0 Response to "what is the name of the 32-bit or 128-bit number that is used to identify a device on a network"
Post a Comment